The computer is a device where you can program your instruction, prefer to do your specified tasks and generate results at a linear speed. A computer is a device that can solve your difficulties and problems, process data, and store data!
The literal meaning of some computers might be a calculator device; it is full of abbreviated machines that are mainly used for training and, as such, education!
However, our modern era has computers that can do many quiet calculations! The computer is a machine that receives some inputs and stores education and research! So in this post, we will be discussing some Disadvantages and Advantages of Computers!
What are Computers and Their Uses?

Computers are incredible machines that help us in so many ways. From storing data to creating presentations, they make our lives easier by performing complex tasks at the click of a button. They work based on our commands and allow us to connect with others, work online, and communicate via the Internet. Understanding how to operate a computer gives us control over this powerful tool.
Uses of a Computer
- Making Calculations: Computers excel at performing calculations. Many mathematical and scientific algorithms are built into their software, making them highly efficient at processing numbers.
- Storing and Retrieving Data: Computers can store vast amounts of data and information, and they provide quick access to this data whenever needed. It’s like having a giant, organized library at your fingertips.
- E-mail and Video Conferencing: Computers are essential for email and video conferencing, helping people stay connected across long distances. Whether it’s a business meeting or catching up with family, computers make it easy.
- Online Shopping: With computers, shopping is just a few clicks away. People can buy goods and services online, often at better prices and with more convenience than shopping in person.
- Word Processing Applications: Creating documents, presentations, and other materials is simple with word processing programs. Programs like Microsoft Word and Google Docs are standard tools for both students and professionals.
- Database Management: Computers are used to store and manage large databases. They help in organizing, processing, and retrieving information efficiently, which is crucial for businesses and organizations. To enhance this process, companies can leverage a Google Cloud ETL solution, which streamlines data integration and transfer.
- Graphics Designing: Designing images, logos, and other visual content is easy with graphic designing software like Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator. Computers help artists bring their creative visions to life.
- Surveillance: Computers are used in surveillance and law enforcement to monitor activities and detect criminal behavior. They play a key role in enhancing security and safety.
- Education: Computers are vital in education, helping to teach students various subjects and explain complex concepts through interactive software and online resources.
- Entertainment: For entertainment, computers offer endless options, such as playing video games, watching movies, listening to music, and browsing the web. They are central to how we relax and have fun.
In today’s tech-smart world, computers are indispensable. From the desktops we use at work to the smartphones in our pockets, they are everywhere. While they bring numerous benefits, it’s also important to be aware of their potential drawbacks and use them wisely.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
Advantages of Computer

- Information of computer: Computers offer access to vast amounts of information, fostering learning besides knowledge-divide
- Research: Conducting profound research converts efficiently and is accessible through online databases and search engines.
- Social media: Excessive shade time can contribute to reduced face-to-face interactions besides social media.
- Privacy: The collection and storage of personal data raises sorrow about privacy besides surveillance.
- Speed: The computer is now more than just a tool for calculations. These days, computers are essential to human existence. The speed at which processers operate is one of their most significant advantages; it allows humans to do their work quickly.
- Multitasking: One of the critical assistances of computers is their skill to multitask. A computer can perform some tasks simultaneously, calculating numerical problems in seconds. The computer system can complete millions or billions of errands in a single second.
- Productivity: Computers can do work very quickly, automatically doubling productivity.
- Communication: Computers help users understand and communicate with other devices more effectively.
- Task Completion: They can complete tasks that might be impossible for humans to do.
- Accuracy: Computers perform not only calculations but also other tasks with high accuracy.
- Data Security: Protecting digital information is a key benefit of computers, known as data security.
Disadvantages of Computer

- Phony news: Numerous ways for sharing data are possible by computers. However, bogus news can be spread using this media. When false information is disseminated among users, numerous claims are filed.
- Internet-Based Crimes: Computers can experience cyber then hacking guilt just like any other gadget. In the world of forward-thinking computers, data theft is one of the most significant risks. It could happen online or on a detachable offline device like USB.
- Health concern: Using computers frequently can result in various health risks—excessive screen time grounds eye strain and dry eyes. Additionally, extended sitting causes neck, back, and health difficulties.
- Work Displacement: Computerization may lead to work loss in specific industries, impacting workers, etc.
- Technical problem: Glitches, crashes, and technical faults can disrupt job flow, and disadvantages cause hindrances.
- Dependency on computers: More reliance on computers can lead to a loss of manual skills and critical overthinking skills.
- Decrease the Job Opportunities: The previous generation did not apply to computers, or they needed the superiority of computers. When computers came into the field, they confronted a considerable journal.
Types of Computer Networks
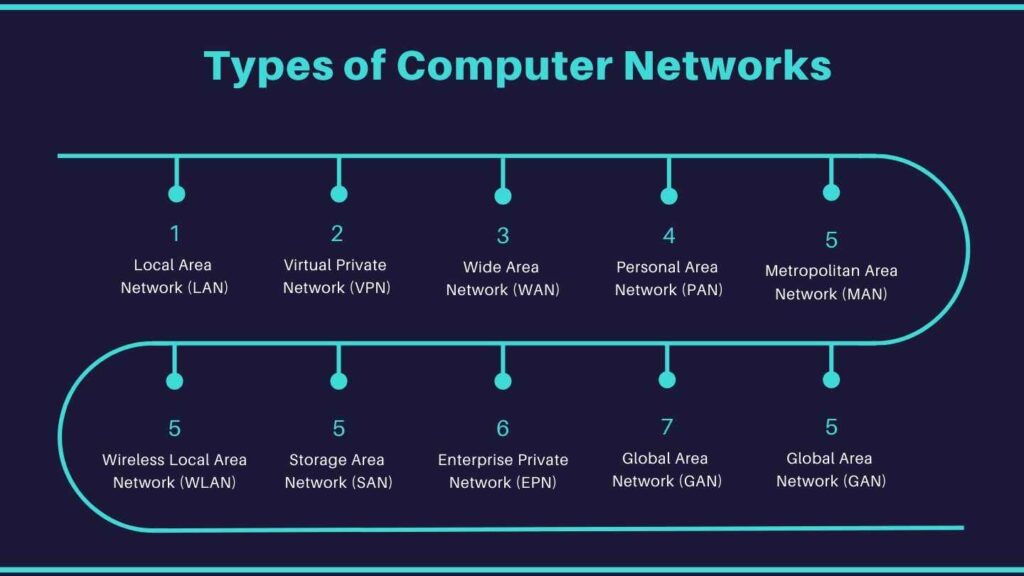
Understanding the types of computer networks helps us grasp how our devices communicate and share information. From the personal connections in a PAN to the vast reach of a GAN, each network type serves a unique purpose and plays a crucial role in our interconnected world.
1. Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network is a step up from a PAN. It covers a small geographical area, like a home, office, or a group of buildings. LANs are used to connect computers and other devices within this area, allowing for resource sharing such as printers, files, and internet access.
Example: The network in a small office building that connects all the computers and printers.
2. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network extends a private network across a public network, such as the Internet. VPNs allow users to send and receive data as if their devices were directly connected to the private network, providing security and privacy.
Example: Remote employees using a VPN to securely access their company’s internal network from home.
3. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network covers a broad geographical area, often a country or continent. WANs are used to connect multiple LANs and MANs, facilitating communication and data transfer over long distances. The internet itself is the largest example of a WAN.
Example: The network connecting different branch offices of a multinational company.
4. Personal Area Network (PAN)
A Personal Area Network is the smallest and most basic type of network. It covers a very limited area, typically within a range of a few meters. PANs are primarily used for connecting personal devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other peripherals. Think of it as your own personal bubble of connectivity.
Example: Bluetooth connections between your phone and wireless headphones or smartwatch.
5. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network spans a larger area than a LAN, typically a city or a large campus. MANs are designed to connect multiple LANs together, providing higher-speed internet and communication services across the metropolitan area.
Example: The network used by a university campus to connect different buildings.
6. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A Wireless Local Area Network is similar to a LAN but uses wireless technology to connect devices. WLANs provide flexibility and mobility, allowing devices to stay connected within the network without the need for physical cables.
Example: Wi-Fi networks in homes, cafes, or airports.
7. Storage Area Network (SAN)
A Storage Area Network is a specialized, high-speed network that connects storage devices to servers. SANs are designed to handle large volumes of data and provide efficient data transfer and storage management.
Example: Networks used in data centers to connect storage systems and servers.
8. Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
An Enterprise Private Network is built and owned by a single organization. EPNs are designed to securely connect various sites and locations of the organization, providing efficient and reliable communication and resource sharing.
Example: The network used by a corporation to connect its headquarters, branch offices, and remote sites.
9. Campus Area Network (CAN)
A Campus Area Network is similar to a MAN but is specific to a single campus or organization, such as a university, large corporate campus, or military base. CANs connect multiple buildings within the campus, providing network access and resources.
Example: The network connecting different departments within a university campus.
10. Global Area Network (GAN)
A Global Area Network is a network that spans the entire globe. GANs connect different types of networks, such as LANs, WANs, and MANs, on an international scale. The internet can also be considered a GAN due to its global reach.
Example: The network infrastructure used by international organizations like the United Nations.
To Sum Up
The efficiency, connectivity, and boundless opportunities computers offer in our contemporary lives. The ease of accessing information, connecting globally, and accomplishing tasks highlights the friendly nature of these electronic companions. But, by adopting a user-friendly mindset, we can transform these challenges into occasions for growth and awareness as we continue our digital journey; the harmony of advantages and disadvantages ensures that the melody of our technological reality remains enriching and balanced.
FAQs

How many disadvantages does a computer have?
Computers are countless tools, but they have their disadvantages, too. They can be slow, unreliable, in addition expensive. They also require constant maintenance besides upgrades.
What are the benefits and harms of computers?
Speed and accuracy: Computers can complete tasks quickly and with high accuracy. Cost: Computers can be pretty luxurious. Storage: Computers can store vast amounts of data in a minor space. Maintenance: Computers require regular upkeep and upgrades.
What is the role of computers in modern society?
Communication then Information Access: Internet and Email: Computers permit instant global communication through email, messaging apps, and video conferencing. They also provide admission to a vast ocean of information on the internet. Social Media: Stages like Facebook and Twitter.
You might also be interested in reading:
