Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and the forms of energy involved in these processes. It explores how thermal energy is converted to and from other forms of energy and how it affects matter.
Importance of Thermodynamics in Engineering and Science
Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in various fields, including mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, aerospace, and environmental science. Understanding thermodynamic principles is essential for designing engines, and refrigerators, and even predicting weather patterns.
Basic Concepts in Thermodynamics
Laws of Thermodynamics
There are four fundamental laws:
- Zeroth Law: Defines thermal equilibrium.
- First Law: Conservation of energy.
- Second Law: Entropy increase principle.
- Third Law: Absolute zero temperature.
Thermodynamic Systems
Thermodynamic systems are classified based on their interactions with the surroundings:
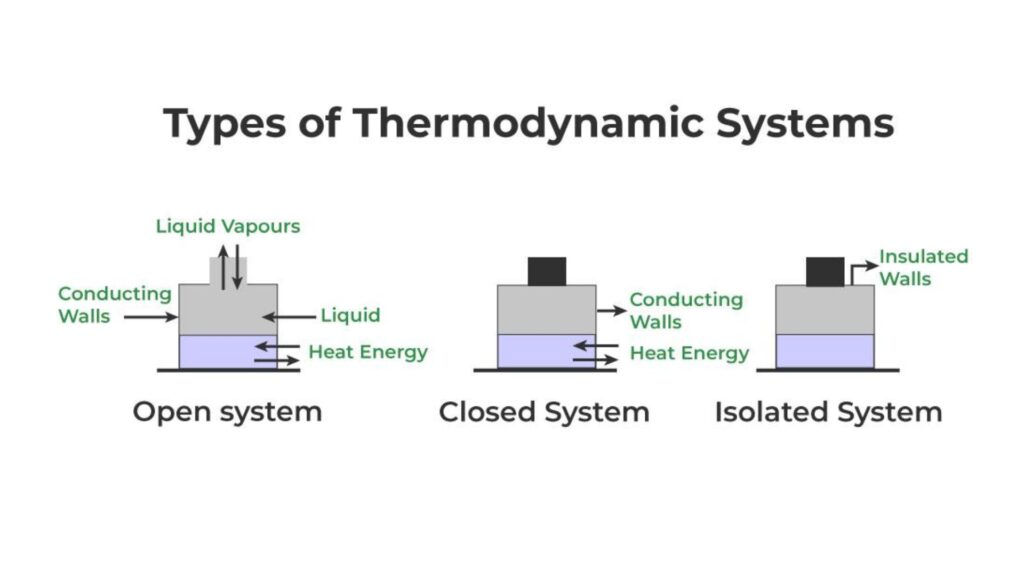
- Open System: An open thermodynamic system can exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings. For example, think of a pot of boiling water on the stove. Here, both heat (energy) and steam (matter) escape into the air.
- Closed System: A closed thermodynamic system can exchange only energy with its surroundings, not matter. Imagine a pressure cooker on the stove with the lid securely closed and the whistle in place. In this case, heat can escape, but steam (matter) cannot. However, once the whistle blows and steam is released, it becomes an open system because both heat and steam are escaping.
- Isolated System: An isolated thermodynamic system cannot exchange either energy or matter with its surroundings. Picture a perfectly insulated cooler. No heat or matter enters or leaves the cooler, making it an isolated system.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Questions
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics states that if two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
Common Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers
Q1: What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
Answer: The Zeroth Law states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they must be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
Q2: How does the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics facilitate temperature measurement?
Answer: It establishes the concept of temperature. If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body (a thermometer), they have the same temperature.
First Law of Thermodynamics Questions
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted. It is essentially the principle of conservation of energy.
Common Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers
Q1: What is the First Law of Thermodynamics?
Answer: The First Law of Thermodynamics states that the total energy of an isolated system is constant; energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
Q2: How does the First Law of Thermodynamics apply to a closed system?
Answer: In a closed system, the change in internal energy equals the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system.
Second Law of Thermodynamics Questions
The Second Law of Thermodynamics introduces the concept of entropy, stating that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time.
Common Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers
Q1: What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
Answer: The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases over time, and processes occur in the direction of increasing entropy.
Q2: Can you explain what entropy is?
Answer: Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. It quantifies the amount of energy in a system that is no longer available to do work.
Third Law of Thermodynamics Questions
The Third Law of Thermodynamics states that as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, the entropy of the system approaches a minimum value.
Common Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers
Q1: What does the Third Law of Thermodynamics state?
Answer: The Third Law states that the entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero temperature is exactly zero.
Q2: Why is the Third Law of Thermodynamics important?
Answer: It provides a reference point for the determination of entropy and helps in understanding the behavior of substances at very low temperatures.
Top 30 Thermodynamics Interview Questions with Answers
Q1. What is the Carnot cycle?
Answer: The Carnot cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that consists of four reversible processes: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and adiabatic compression.
Q2. Describe different types of thermodynamic cycles.
Answer: Different types of thermodynamic cycles include the Carnot cycle, Rankine cycle, Otto cycle, and Diesel cycle.
Q3. How does a refrigeration cycle work?
Answer: A refrigeration cycle works by removing heat from a low-temperature space and transferring it to a high-temperature space using a refrigerant.
Q4. How does a condenser work in a refrigeration system?
Answer: A condenser in a refrigeration system works by removing heat from the refrigerant and converting it back into liquid form.
Q5. How does an air conditioning system work?
Answer: An air conditioning system works by removing heat from indoor air and transferring it outside, resulting in cool air inside.
Q6. What is a heat pump?
Answer: A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one location to another using mechanical work.
Q7. How does a steam turbine work?
Answer: A steam turbine works by converting the thermal energy in steam into mechanical work.
Q8. Describe the Brayton cycle.
Answer: The Brayton cycle is a thermodynamic cycle used in gas turbine engines and consists of four processes: compression, constant-pressure heating, expansion, and constant-pressure cooling.
Q9. What is the Rankine cycle?
Answer: The Rankine cycle is a thermodynamic cycle used in power plants to convert heat into mechanical work.
Q10. What are the different types of heat exchangers?
Answer: The different types of heat exchangers include shell and tube exchangers, plate exchangers, and finned tube exchangers.
Q11. What is heat exchanger effectiveness?
Answer: Heat exchanger effectiveness measures the actual heat transfer compared to the maximum possible heat transfer.
Q12. Explain superheating and subcooling.
Answer: Superheating refers to heating a substance above its boiling point without changing its phase, while subcooling refers to cooling a substance below its condensing point without changing its phase.
Q13. Explain the concept of latent heat.
Answer: Latent heat refers to the amount of heat required or released during a phase change at constant temperature.
Q14. Explain the concept of specific heat capacity.
Answer: Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius.
Q15. Explain the concept of entropy.
Answer: Entropy measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system.
Q16. What is the Clausius-Clapeyron equation used for?
Answer: The Clausius-Clapeyron equation is used to derive relationships between temperature, pressure, and changes in state for substances undergoing phase changes.
Q17. How do you calculate efficiency in a thermodynamic system?
Answer: Efficiency is calculated by dividing the useful output energy by the input energy and multiplying it by 100%.
Q18. Explain the concept of the steady-state flow energy equation.
Answer: The steady-state flow energy equation is an energy balance equation used to analyze fluid flow systems.
Q19. What are the different types of thermodynamic processes?
Answer: The different types of thermodynamic processes include isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, and isochoric processes.
Q20. What factors affect thermal conductivity?
Answer: Factors that affect thermal conductivity include temperature, material properties, and sample dimensions.
Q21. How does a cooling tower work in a power plant?
Answer: A cooling tower in a power plant works by removing excess heat from condenser water through evaporation.
Q22. What are the different types of fuels used in power plants?
Answer: The different types of fuels used in power plants include coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear fuel.
Q23. How does thermodynamics relate to renewable energy sources?
Answer: Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in understanding and improving renewable energy technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems by analyzing efficiency and maximizing energy conversion.
Q24. What are some applications of thermodynamics in everyday life?
Answer: Applications of thermodynamics in everyday life include refrigerators, air conditioners, engines, and heating systems.
Q25. What are some challenges in thermodynamics engineering?
Answer: Some challenges include optimizing energy efficiency, minimizing losses during energy conversion processes, managing complex systems with multiple variables, and developing sustainable solutions to address environmental concerns.
Q26. Can you discuss any experiences or projects related to thermodynamics?
Answer: Highlight any relevant academic projects or industry experiences where you applied thermodynamics principles or worked on projects involving energy transfer or conversion.
Q27. How do you stay updated with advancements in thermodynamics engineering?
Answer: Mention your proactive approach to staying informed about industry trends by regularly reading research papers, attending conferences or webinars, and being part of professional engineering organizations.
Q28. Can you differentiate between an open system and a closed system?
Answer: An open system allows matter and energy to be exchanged with its surroundings, while a closed system only allows energy transfer but not matter exchange.
Q29: What is enthalpy?
Answer: Enthalpy is the heat content of a system at constant pressure, defined as the sum of the internal energy and the product of pressure and volume (H = U + PV).
Q30: How does entropy relate to the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
Answer: Entropy quantifies the level of disorder or randomness. The Second Law states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases, leading to spontaneous processes.
Conclusion
Thermodynamics is a vast and complex field that forms the backbone of many engineering and scientific principles. Understanding its core concepts and laws is essential for solving real-world problems and excelling in technical interviews.
Read More:






